- News
23 May 2019
Toyoda Gosei doubles operating current in vertical GaN power device from 50A to 100A
Toyoda Gosei Co Ltd of Kiyosu, Aichi Prefecture, Japan has developed a vertical gallium nitride (GaN) power semiconductor device with high current operation of 100A on a single chip, one of the highest levels yet achieved, it is claimed.
In addition to applications as electronic components for power conversion in home appliances, mobility, industry etc, the proliferation of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy has been boosting demand for power devices with higher performance. With the silicon used in conventional devices however, it is difficult to significantly improve efficiency in converting high power. Specifically, after half a century of improvements, the balance between high breakdown voltage and low electrical resistance is approaching its limits due to the physical properties of silicon, making it difficult to achieve further significant reductions in conduction loss during high-power operation and in switching loss during high-frequency operation.
Toyoda Gosei has sought to overcome this by using GaN, which has the physical property of high breakdown voltage (more than 10 times that of silicon), and a chip structure in which electricity flows vertically to the GaN substrate. This material and structure combination allows thinner and smaller device designs and other improvements that lead to higher performance. In particular, with thinner, lower-resistance GaN, conduction loss can be reduced. Also, with a vertical structure, the entire chip is used in current flow, making it possible to make semiconductors smaller and to reduce switching loss. With this combination, Toyoda Gosei has achieved high breakdown voltage (1.2kV level) and low resistance (1.8mΩcm2), and high-frequency operation (≥10MHz).
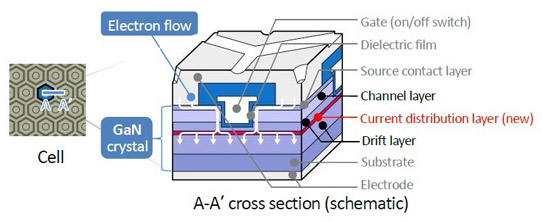
The firm’s latest development, which has doubled the electric current capacity from the previous 50A to 100A on a single chip, results from the introduction of a new current distribution layer that lowers electric resistance by expanding the flow of electricity on the drift layer. This new technology was presented at the 31st IEEE International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and ICs (ISPSD 2019) in Shanghai, China (19-23 May).
Toyoda Gosei says that it aims to continue improving the reliability and other qualities of the devices for their early commercialization, in collaboration with manufacturers in power electronics.
Toyoda Gosei achieves high-current operation with vertical GaN power semiconductors
Toyoda Gosei develops high-voltage GaN power semiconductor device for large-current operation
Reducing on-resistance in vertical gallium nitride MOSFETs
Toyoda Gosei Power electronics Vertical GaN transistors


