- News
13 December 2012
First PV cells from Solliance’s CIGS facility yield 13.85% efficiency
At the new copper indium gallium (di)selenide (CIGS) facility of the Solliance collaboration platform in Eindhoven, The Netherlands, the first CIGS solar cells have been fabricated, demonstrating solar energy conversion efficiency of 13.85%. The result is expected to be the starting point for further improvements in the cell’s efficiency, large-area uniformity and run-to-run variability. The facility will also be used for advancing Solliance’s alternative thin-film photovoltaic (TF-PV) activities.
The alliance partners involved in Solliance include ECN (the energy research institute of The Netherlands), TNO (the Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research in Delft), the Holst Center in Eindhoven (a joint research initiative of Imec and TNO), TU/e (Eindhoven University of Technology) and nanoelectronics research institute Imec of Leuven, Belgium. Solliance is supported by the Dutch province of North Brabant, which dedicated €28m to fund a large shared laboratory in Eindhoven (complementing the partner’s labs, which are also available to the other partners).
Solliance works in cooperation with industry, both to fulfill its short-term needs and on mid- and long-term research programs. It focuses on three main thin-film technologies: thin-film silicon, copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS), and organic photovoltaics (OPV). For these principal themes, Solliance is collaborating with industry at its facilities in Eindhoven as well as at Imec’s facilities in Leuven. Solliance also concentrates on generic technologies vital to the thin-film PV industry, including testing, characterization and monitoring, laser technologies, transparent conductive layers, monolithic interconnection, thin-film deposition techniques, roll-to-roll processing, and in-line monitoring.
Solliance’s aim is to strengthen the position of the Eindhoven–Leuven–Aachen triangle (the ELAT region) as a world player in thin-film PV by joint use of infrastructure, alignment of research programs, and close cooperation with the solar TF-PV business community.
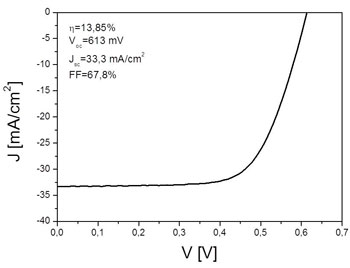 Figure 1:
CIGS solar cell with 13.85% efficiency, fabricated in Solliance’s new CIGS facility.
Figure 1:
CIGS solar cell with 13.85% efficiency, fabricated in Solliance’s new CIGS facility.
In September, the last tool of the CIGS solar base-line facility was installed and accepted at TNO in Eindhoven. A reference process flow has since developed, resulting in the first CIGS TF-PV cells fully made with the facility’s equipment. The highest efficiency obtained by the first full run was 13.85%. This is similar to industrial CIGS modules (with an efficiency of 13-14%), but still below the laboratory record of 20.3% on a CIGS solar cell reported in August 2010 by Zentrum für Sonnenenergie- und Wasserstoff-Forschung Baden-Württemberg (Centre for Solar Energy and Hydrogen Research, ZSW) in Stuttgart, Germany. Based on Solliance’s result, further improvements in cell efficiencies are expected in the coming months through intensified collaboration between TNO and Imec in the CIGS facility.
The facility’s main focus will be on improving the large-area uniformity and reducing the run-to-run variability of CIGS solar cell manufacturing. The stable and reproducible reference process flow to be obtained will then serve as a baseline for developing improved cell concepts and for innovating process equipment for individual process steps. The facility possesses all the processing tools for a full CIGS solar cell flow on substrates up to 30cm x 30cm, and will be used as a pre-pilotline for testing cell and process equipment concepts.
Solliance’s CIGS facility will also be used for the alternative TF-PV activities of Solliance, aiming to improve the solar cell efficiency of emerging copper zinc tin sulfide (CZTS) absorber TF-PV materials. This new absorber is expected to solve the availability problem of the In and Ga material of the CIGS absorber when these are used in high-volume manufacturing. The new CZTS absorber material consists of only Earth-abundant elements such as Cu, Zn, Sn, Se and S. Imec’s thin-film solar cell activities, focusing on CZTS and organic PV, are integrated into the Solliance collaboration platform.


