- News
17 April 2012
Sumitomo Electric building demo megawatt CPV power generation/storage system
Sumitomo Electric Industries Ltd (SEI) has developed a megawatt-class electric power generation/storage system consisting of what is claimed to be the world’s largest redox flow battery and Japan's largest concentrated photovoltaic (CPV) units. The firm is currently constructing a facility to test the system at its Yokohama Works (Sakae-ku Yokohama), aiming to start the demonstration in July.
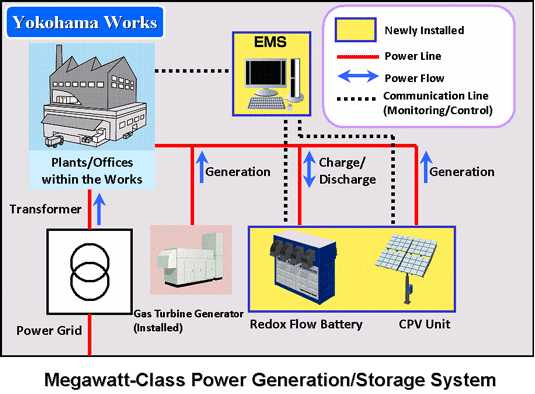
Image: Megawatt-class power generation/storage system.
To meet the expected growth in demand for distributed power systems using renewable, SEI has been working on R&D of technology for effective power conversion/control and generation/storage. As part of its development, the firm started testing its micro smart-grid system at the Osaka Works last June. In this system, natural energy sources - including an in-house developed CPV system and a small redox flow battery - are DC-interconnected, and the energy management system (EMS) controls fluctuations in natural energy (excluding solar and wind power) and power consumption by relatively small electric loads (excluding lighting and home appliances). Consequently, the overall system enables the most reliable and efficient power control, particularly from the viewpoint of general consumers, it is claimed.
Recently, there has also been increasing expectation for major energy consumers, such as plants and companies, to promote the use of renewable energy and energy saving measures. In view of this, SEI has developed a large-scale electric power generation/storage system consisting of a redox flow battery and CPV units. The system with megawatt-level capacity and output power will be tested at the Yokohama Works with the aim of accelerating the development and commercialization of large power systems and related facilities.
The system consists of 28 CPV units (giving maximum total power generation of 200kW) as energy sources and one redox flow battery (with a capacity of 1MW for 5 hours) as a storage facility for the CPV-generated power and low-cost electricity provided by power companies during the night, while connected to external commercial power networks. Using the EMS, the system aims to regulate the amount of electricity provided by power companies using the redox flow battery's charge/discharge control function. The system also targets systematic use of solar power by using the battery to balance the fluctuations in CPV power generation (which is susceptible to the weather).
The redox flow battery is a storage battery consisting of a charging/discharging cell section and a tank full of metal ion electrolyte. It charges/discharges through oxidation-reduction of vanadium or other ions. The battery has a long service life, as the electrodes and electrolyte are not subject to deterioration even after repeated charge/discharge operations. It is also easily maintained, as its uses the same electrolyte in both the cathode and anode. The battery is also claimed to provide increased safety, as it does not require any combustible substances and is operated at ambient temperatures. It is suitable for irregular, highly fluctuating charge/discharge operations, enabling accurate monitoring and control of stored electric power. Accordingly, it is an optimal storage battery for efficient use of renewable energy and surplus electricity supplied during the night, the firm claims.
The CPV unit is a photovoltaic system incorporating small-size photovoltaic cells for energy conversion, directing high-intensity sunlight converged by a lens to photovoltaic cells.Ssince the CPV cells are made from compound semiconductor material, the power generation efficiency of the CPV panel is reckoned to be about twice that of silicon solar panels currently on the market. Installed in an elevated position, CPV panels provide a usable space beneath them. The newly developed CPV unit offers 7.5 times more output power (7.5kW/unit), yet the CPV panels are thinner and lighter than conventional panels.
The EMS monitors the amounts of electric power generated by the 28 CPV units, via commercial power networks, stored in a redox flow battery, and consumed at an office or plant in order to manage the electric power flow. The data that is obtained is sent by optical communication networks to be collectively controlled at the central control server. This system will be used in the demonstration test at Yokohama to achieve optimal balance between supply and demand (with maximum demand control of 1MW) as well as power demand control based on preset schedules.
