- News
5 December 2011
3S’ lasers in Curiosity rover launched aboard NASA’s Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft
3S Photonics Group of Nozay, France, which makes chips, optical discrete modules and passive components for the laser, sensing and telecom markets, has provided laser technology for NASA’s MSL (Mars Science Laboratory) mission, which aims to land and operate the rover Curiosity (a mobile robot equipped with 10 instruments) on the surface of Mars, to find out if the planet has ever been inhabited.
The MSL (carrying Curiosity) was launched on 26 November onboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
The CNES, French Space Agency, in partnership with Quantel group and the CESR (French Space Research Institute based in Toulouse) have designed and built two of the 10 instruments on board Curiosity, including the ChemCam (CHEMistry CAMera).
ChemCam is an elementary instrument that analyzes the rocks and the ground around the vehicle up to 9m away. It uses a spectroscopic analysis technique led by laser ablation. A laser shot fires at a target, causing the material to melt and plasma to emerge, which can be detected from a distance via UV-visible spectroscopy. This new technology, which has never been used before, will enable the first selective analysis of Mars’ rocks to be carried out without the need to move the rover. Based on the information retrieved from ChemCam, the rover can reposition itself near to any rock in order to carry out further analysis.
3S Photonics says that, in 2004-2005, its laser diodes were selected and integrated into ChemCam‘s laser for spectroscopy specifically because of the process control and performance and the high reliability of its products (key criteria for the mission).
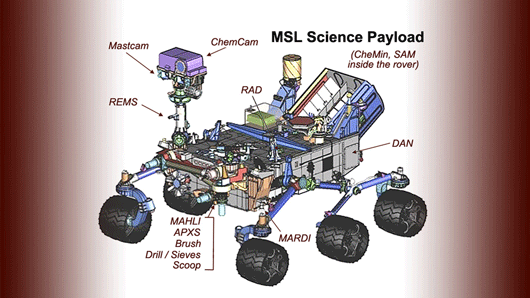
Picture: Drawing of the Mars Science Laboratory mission's rover, Curiosity, showing thelocation of scientific instruments, including ChemCam. Image Credit: NASA.
