
| Home | About Us | Contribute | Bookstore | Advertising | Subscribe for Free NOW! |
| News Archive | Features | Events | Recruitment | Directory |
| FREE subscription |
| Subscribe for free to receive each issue of Semiconductor Today magazine and weekly news brief. |
News
15 June 2009
Fujitsu claims first 100W X-band high-output amplifier with efficiency over 50%
At last week’s IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS2009) in Boston, Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd of Kawasaki, Japan reported the development of a gallium nitride (GaN) high-electron-mobility transistor (HEMT) amplifier that it claims is the first 101 Watt X-band (8-12GHz) high-output amplifier achieving record efficiency of 53%.
 According to comparisons made by Fujitsu, this output is about four times greater than that generated by gallium arsenide (GaAs) HEMT amplifiers, allowing the transmission range to be extended by up to two-fold. Also, compared to GaAs HEMT X-band amplifiers with same-class output power, the new GaN HEMT amplifier can significantly reduce power dissipation.
According to comparisons made by Fujitsu, this output is about four times greater than that generated by gallium arsenide (GaAs) HEMT amplifiers, allowing the transmission range to be extended by up to two-fold. Also, compared to GaAs HEMT X-band amplifiers with same-class output power, the new GaN HEMT amplifier can significantly reduce power dissipation.
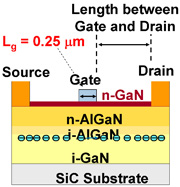
Figure 1: Fujitsu’s new X-band GaN HEMT.
Furthermore, using the amplifier in the C band (4-8GHz), Fujitsu Laboratories has raised its own C-band GaN HEMT amplifier output power record from 320W (reported last October at the 2008 IEEE Compound Semiconductor IC Symposium in Monterey, CA) to 343W (outperforming GaAs-based amplifiers by a factor of seven, according to comparisons made by Fujitsu Labs), while maintaining the level of efficiency. Compared to conventional amplifiers using GaAs HEMTs, the GaN HEMT-based amplifier is therefore expected to extend the transmission range by 2.6-fold in the C band.
The C band is used mostly for fixed-point wireless and wireless access. The higher-resolution X-band is used for weather radar and aircraft control but, because the X band is prone to signal attenuation by rainfall, it needs high amplifier output and efficiency.
Previously reported high-output X-band amplifiers based on GaN HEMTs suffered from poor efficiency, and presented the following problems that need to be solved for practical implementation:
- To achieve high efficiency, the amplifier must have high gain, i.e. the performance of the transistor chip must be improved.
- Transistor chips in high-output amplifiers consist of multiple transistors connected in parallel. If there is a single point of input and output, then a phase discrepancy can be caused between the signal passing down the center of the chip and the signal passing along its periphery due to the different signal path lengths. So, especially for higher frequencies, transistors are operating out of phase with each other, and the full benefit of each transistor cannot be realized. Eliminating this phase discrepancy is necessary to achieve high efficiency.
Fujitsu’s new high-efficiency, high-output GaN HEMT amplifier for the X and C bands consists of two transistor chips. This design enables the inherent high-output performance of GaN HEMTs to come through even at high frequencies, and for them to operate with high efficiency, says Fujitsu. Benefits of the new amplifier include the following:
- To accommodate high frequencies, the gate length was reduced to 0.25µm and the gate-drain gap was optimized, resulting in a high-output transistor featuring good high-frequency characteristics and high breakdown voltage (Figure 1). This enables roughly ten-fold gain in the X band, reduces the resistive component, and raises efficiency.
-
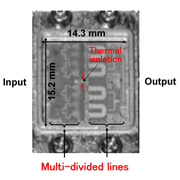 The manifold I/O path structure developed for the C-band GaN HEMT developed last year (which avoided phase discrepancies in the input signal) was further optimized for application to the X band (Figure 2). This eliminated phase discrepancies introduced to the input signal within the chip for the X band as well, enabling uniform performance for a GaN HEMT with high output power density and efficiency. Furthermore, by suppressing thermal interference between the two chips, the performance degradation caused by chip heating was also suppressed.
The manifold I/O path structure developed for the C-band GaN HEMT developed last year (which avoided phase discrepancies in the input signal) was further optimized for application to the X band (Figure 2). This eliminated phase discrepancies introduced to the input signal within the chip for the X band as well, enabling uniform performance for a GaN HEMT with high output power density and efficiency. Furthermore, by suppressing thermal interference between the two chips, the performance degradation caused by chip heating was also suppressed.
Figure 2 (above): Circuit structure of Fujitsu’s new amplifier.
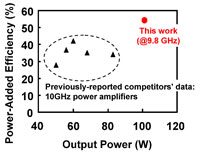 Efficiency is especially important for reducing the transmitter’s power consumption. Compared to previously reported results, with equivalent output in the 10GHz band, efficiency was about 20% higher (see Figure 3), claims Fujitsu, contributing significantly to power savings.
Efficiency is especially important for reducing the transmitter’s power consumption. Compared to previously reported results, with equivalent output in the 10GHz band, efficiency was about 20% higher (see Figure 3), claims Fujitsu, contributing significantly to power savings.
Figure 3 (above): X-band high-output amplifier performance comparison (10GHz band).
Fujitsu says that the results for the new amplifiers raise the prospect of applying the technology to a wide range of applications that demand the combination of high-output and high-efficiency performance. This includes using them as alternatives to traveling-wave tube amplifiers (vacuum tubes commonly used for high-output-power microwave applications), which would enable the realization of smaller, lightweight, more energy-efficient and longer-lasting transmission systems used in weather and air-traffic control radars, satellite transmitters, and next-generation mobile-phone base-stations for wireless communications equipment.
See related items:
Fujitsu reports record 320W C-band power amplifiers
Fujitsu claims first high-output GaN HEMT to cut power in standby mode
![]() Search: Fujitsu Laboratories GaN HEMT X-band GaAs HEMT
Search: Fujitsu Laboratories GaN HEMT X-band GaAs HEMT
Visit: http://jp.fujitsu.com/group/labs/en